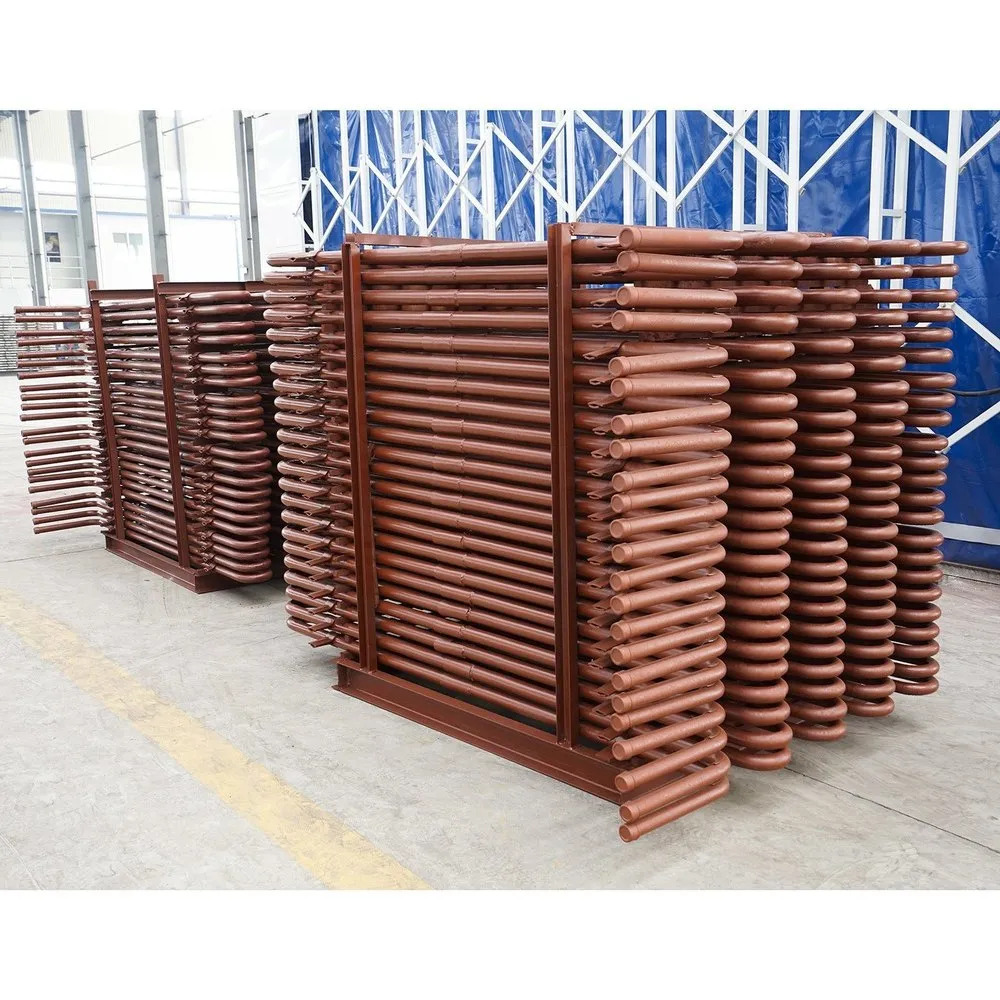
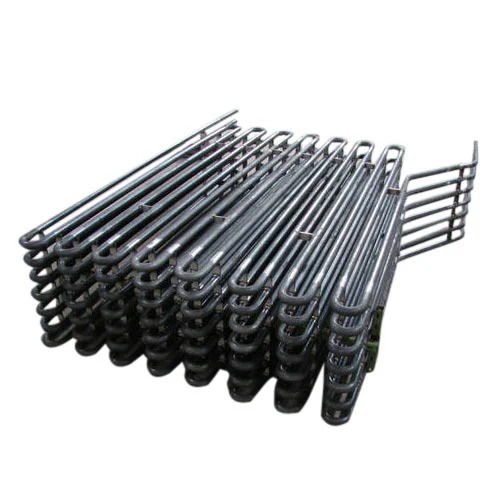
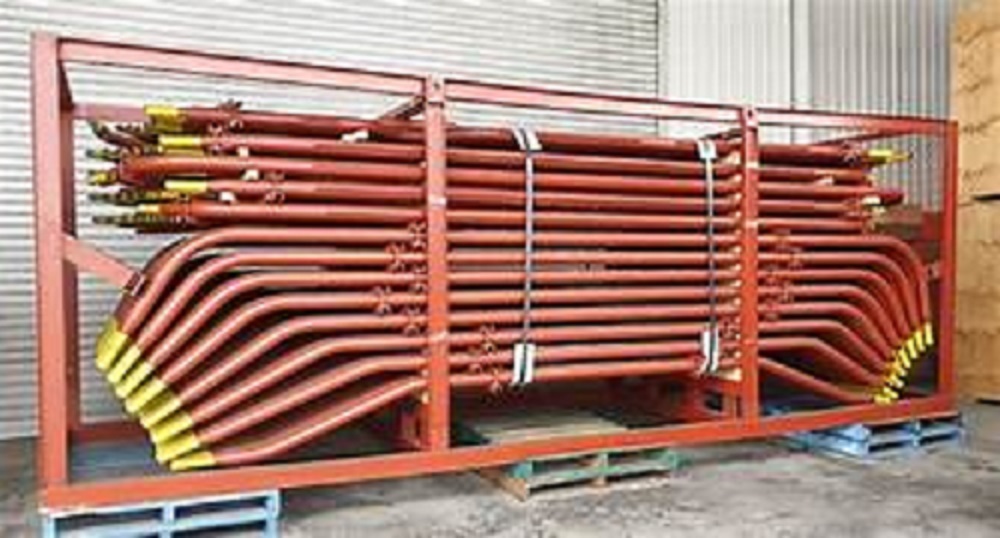
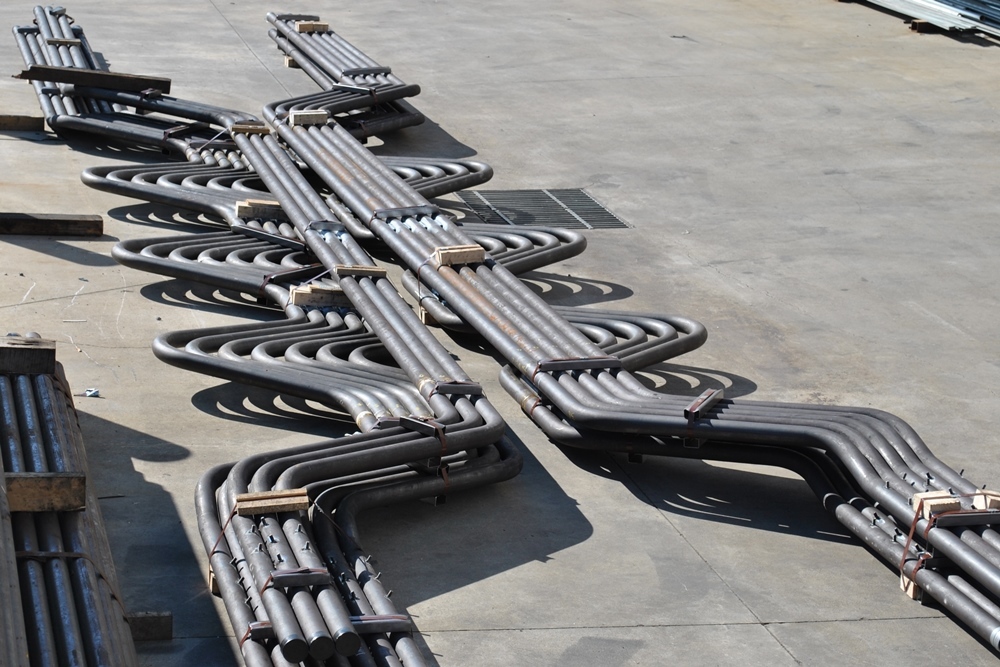
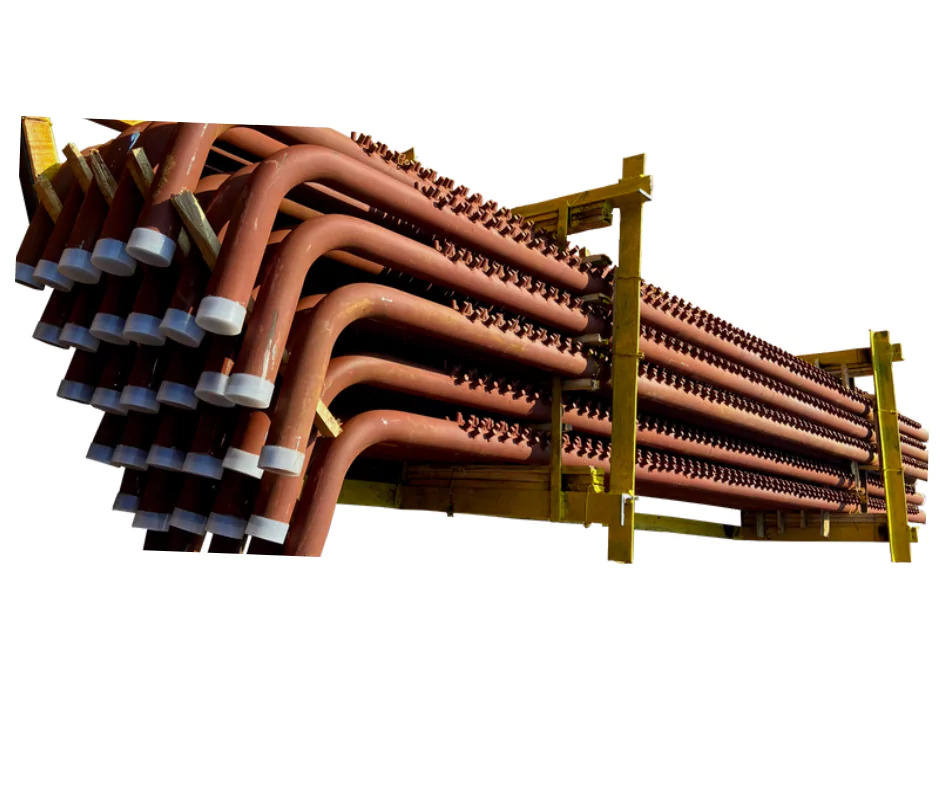
Economizer Coils
Product Details:
- Smell Odorless / Metallic
- Shelf Life Long Lifespan (Subject to operational and maintenance conditions)
- Color Metallic / Silver / Grey
- HS Code 84029020
- Poisonous NO
- Storage Dry, covered storage to prevent corrosion
- Medicine Name Economizer Coils
- Click to View more
Economizer Coils Price And Quantity
- 100000 INR/Unit
- 1 Unit
Economizer Coils Product Specifications
- Dry, covered storage to prevent corrosion
- Used to recover heat from flue gases in various boiler systems
- Tube Bundle Assembly
- Solid
- Economizer Coils
- Metallic / Silver / Grey
- Industrial Grade
- Odorless / Metallic
- Long Lifespan (Subject to operational and maintenance conditions)
- Heat Exchanger Coil
- NO
- 84029020
Economizer Coils Trade Information
- Vadodara
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- 10 Unit Per Week
- 7 Week
- Yes
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Standard Industrial Pack
- Asia
- , All India, South India, Central India, West India, North India, East India, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu, Goa, Jharkhand, Odisha, Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Pondicherry, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
- ISO
Product Description
What Are Economizer Coils?
Economizer coils are tubular heat exchangers located in the flue gas path (after combustion but before exhaust). They preheat the boiler feedwater using the otherwise wasted heat from the flue gases.
Purpose of Economizer Coils:
-
Increase boiler efficiency (by 3to10%)
-
Reduce fuel consumption
-
Lower flue gas temperature
-
Reduce operating costs
-
Minimize environmental emissions (like CO)
Construction:
-
Material: Carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel (depends on flue gas conditions)
-
Tube shape: Bare or finned tubes (fins increase surface area and heat transfer)
-
Arrangement: Horizontal or vertical, depending on boiler design
Working Principle:
-
Hot flue gases from the boiler pass over the economizer coils.
-
Cooler feedwater flows inside the coils.
-
Heat transfers from gas to water.
-
Water enters the boiler at a higher temperature, reducing fuel needed for steam generation.
Applications:
-
Power plants (coal, gas, biomass)
-
Industrial steam boilers
-
Heat recovery steam generators (HRSGs)
-
Marine boilers
-
Common Issues:
-
Fouling/soot accumulation (reduces heat transfer)
-
Corrosion (from acidic flue gases)
-
Leakage (due to thermal stress or corrosion)
-
Tube rupture (from overheating or pressure imbalance)
-
Maintenance Tips:
-
Regular cleaning (soot blowers or manual)
-
Inspection for corrosion and scaling
-
Water chemistry control
-
Periodic non-destructive testing (NDT)
-
-
High Performance Heat Recovery
Designed for optimal heat transfer, these economizer coils capture waste heat from flue gas streams in boilers, significantly improving overall system efficiency while reducing energy consumption and operational costs. Their customizable tube and fin configurations allow adaptation to diverse applications.
Robust Construction and Versatile Materials
Utilizing premium carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel for tubes, and a choice of aluminum, copper, or stainless steel fins, these coils combine durability with high thermal conductivity. Each coil is built to international standards, ensuring reliability and performance under demanding industrial conditions.
Tailor-Made Solutions and Simple Maintenance
With a fully customizable design, including tube diameter, thickness, and fin type, these coils are crafted to meet specific project requirements. Their tube bundle assembly design enables straightforward cleaning and servicing, extending operational lifespan and ensuring safe, efficient use.
FAQ's of Economizer Coils:
Q: How are economizer coils used in boiler systems?
A: Economizer coils are installed in boiler flue gas paths to recover residual heat from exhaust gases. This recovered thermal energy preheats incoming feedwater, increasing boiler efficiency and reducing fuel consumption in power plants and industrial heating setups.Q: What materials are available for economizer coil tubes and fins?
A: The tube materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel, while fin options comprise aluminum, copper, or stainless steel. The choice depends on the application's thermal, pressure, and corrosion resistance requirements.Q: When should I opt for additional corrosion protection or galvanized finish?
A: Corrosion protection or a galvanized finish is advisable when operating in corrosive environments or handling aggressive flue gases. This extends the coil lifespan and maintains system efficiency by preventing premature deterioration.Q: Where are economizer coils typically installed?
A: These coils are most commonly installed in the exhaust section of boilers or heat recovery units in power plants, industrial heating processes, or any system aiming to optimize energy usage by reclaiming heat from flue gases.Q: What is the process for cleaning and maintaining economizer coils?
A: Routine cleaning involves removing soot or deposits from the tube and fin surfaces, typically using compressed air, chemical cleaning, or mechanical brushes. Regular inspection ensures reliable operation and allows early detection of wear or fouling.Q: What are the benefits of using economizer coils?
A: Using economizer coils leads to reduced fuel costs, lower emissions, improved boiler performance, and longer equipment life. Recovering waste heat translates to substantial energy savings and environmental benefits.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Boiler Pressure Part' category
 |
SHREE NARAYAN ENTERPRISE
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese