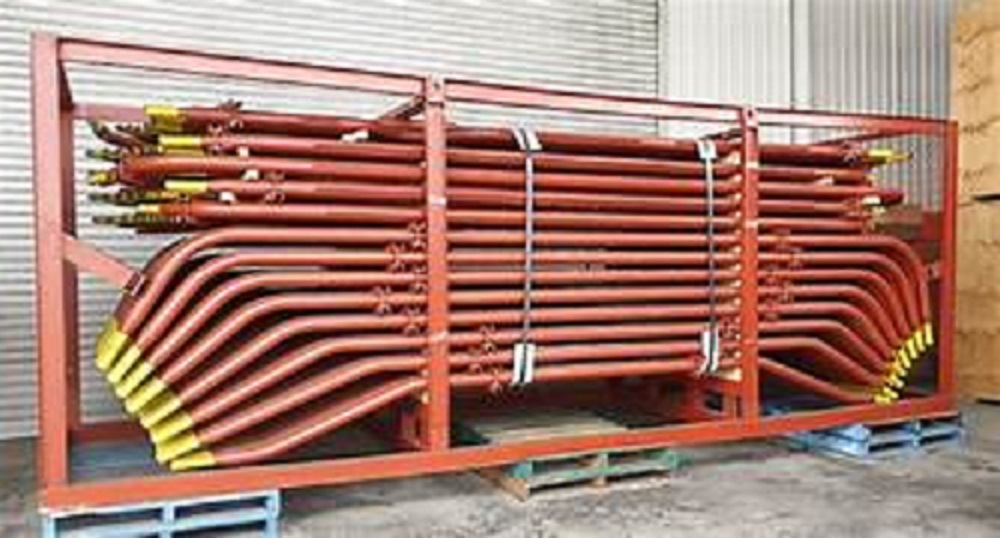
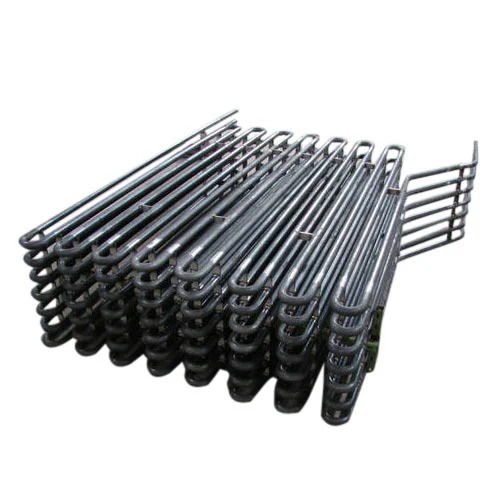
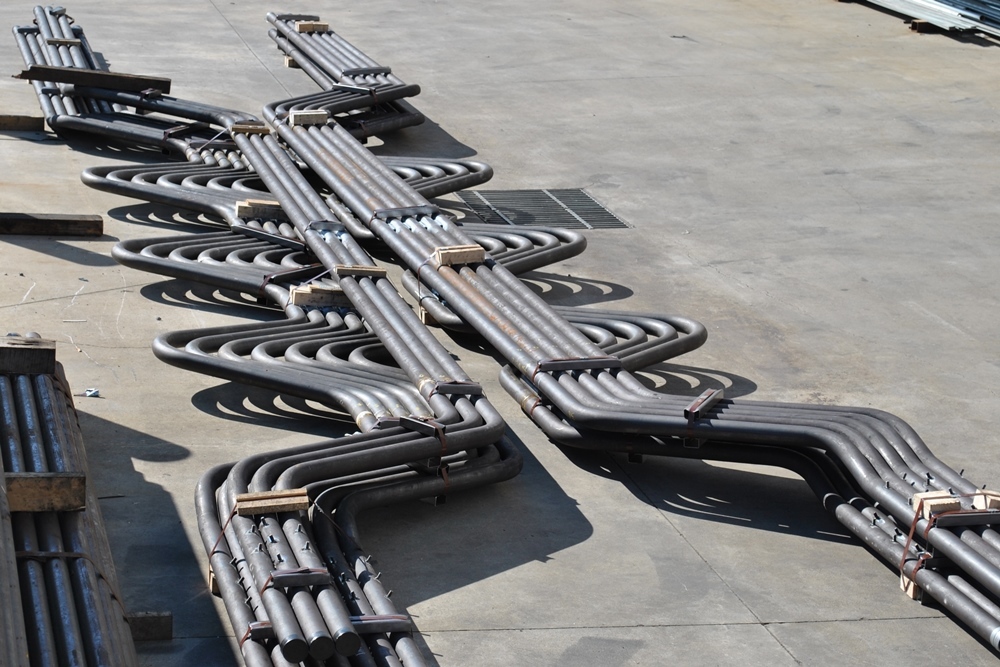
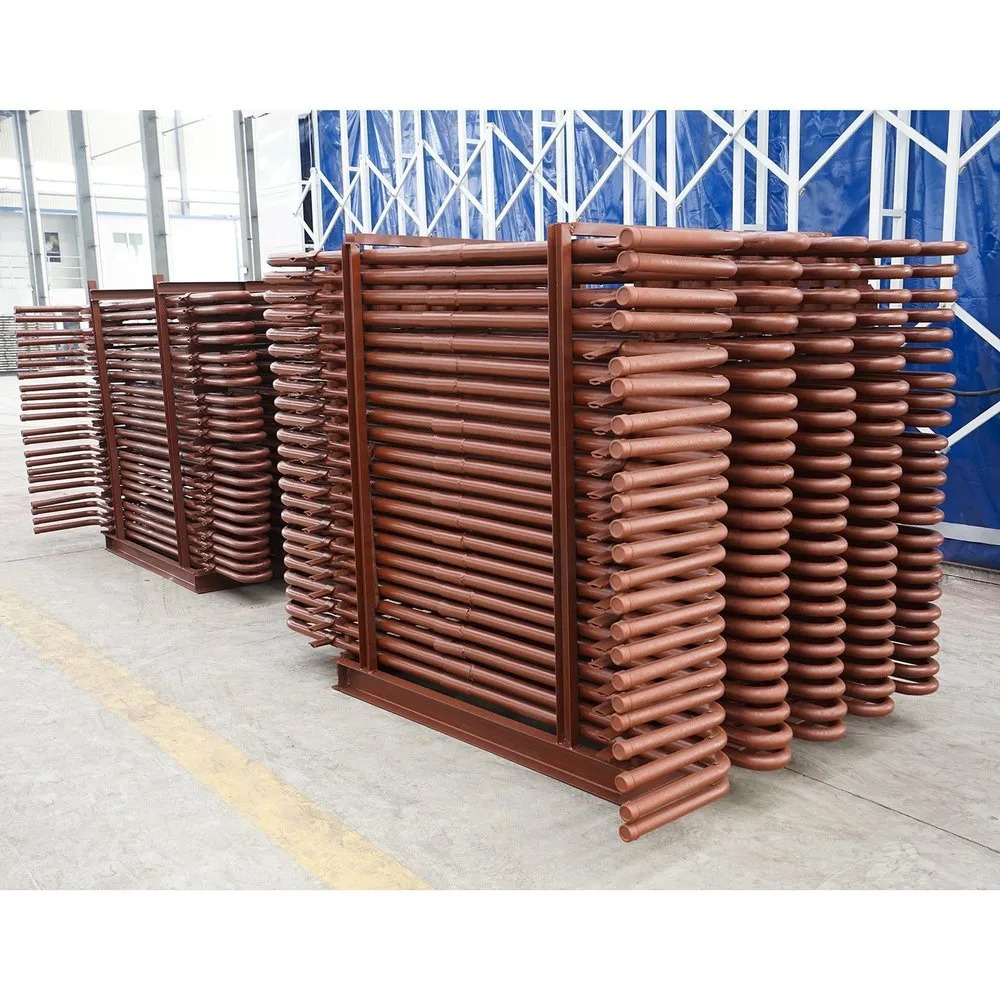
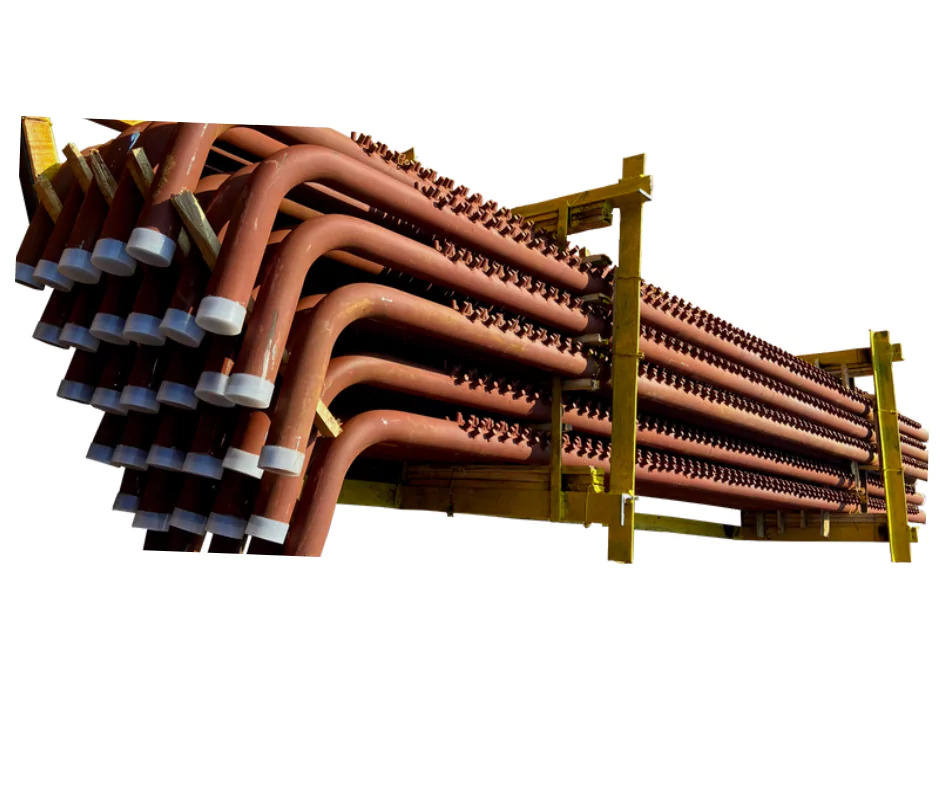
Boiler Bank tubes
Product Details:
- Storage Store in dry, covered area away from moisture
- Poisonous Non-Poisonous
- Melting Point Approx. 14251540C (for carbon steel)
- HS Code 7304
- Smell Odorless (Metal)
- Shelf Life Long shelf life if properly stored (typically >5 years)
- Solubility Insoluble in water
- Click to View more
Boiler Bank tubes Price And Quantity
- 1 Unit
- 100000 INR/Unit
Boiler Bank tubes Product Specifications
- Insoluble in water
- Metallic Grey / Black finished
- Approx. 14251540C (for carbon steel)
- Boiler Bank Tubes
- Long shelf life if properly stored (typically >5 years)
- Solid (Metal Tubes)
- Heat exchange tubes in water-tube boilers and steam boilers
- Non-Poisonous
- Smooth and round tube structure, free from defects
- Seamless / ERW, Various Grades (e.g., SA 210 Gr A1, SA 213, SA 178)
- 7304
- Odorless (Metal)
- Store in dry, covered area away from moisture
Boiler Bank tubes Trade Information
- Vadodara
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- 100 Unit Per Day
- 7 Days
- Yes
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Standard Pack
- Asia
- , All India, South India, Central India, West India, North India, East India, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu, Goa, Jharkhand, Odisha, Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Pondicherry, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
- IBR
Product Description
Boiler Bank Tubes Complete Guide
Boiler bank tubes, also known as generating bank tubes, are a central part of the steam generation system in water-tube boilers. They connect the steam drum and the mud drum and play a vital role in producing saturated steam by transferring heat from flue gases to the circulating water inside the tubes.
What Are Boiler Bank Tubes?
Boiler bank tubes are straight or slightly curved water tubes arranged in parallel rows (banks) between the upper steam drum and the lower mud drum. They're exposed primarily to convection heat from the flue gases, and their main purpose is to:
-
Generate saturated steam
-
Complete the water/steam circulation loop
-
Improve boiler efficiency
Typical Arrangement:
-
Position: Located between the furnace and economizer, in the convective pass of the boiler.
-
Orientation: Generally vertical, but some boilers may use slightly inclined tubes for circulation efficiency.
-
Tube Banks: Often arranged in multiple rows (front and rear) to increase heat transfer surface.
Design & Material:
-
Tube Material: Usually carbon steel (e.g., SA-210 Gr A1, SA-192) or low alloy steel
-
Tube OD: Common sizes include 38 mm (1.5"), 50.8 mm (2"), 63.5 mm (2.5")
-
Wall Thickness: Varies depending on pressure rating, usually 2.5 mm 4.5 mm
-
Length: Custom to boiler height
-
Connection: Expanded or welded into steam and mud drums
Working Principle:
-
Feedwater enters the mud drum.
-
Water rises through boiler bank tubes, absorbing heat from the flue gases.
-
As water heats up, steam starts forming inside the tubes.
-
The steam-water mixture reaches the steam drum, where steam separates from water.
-
Steam continues to superheater, while water recirculates back.
Function in Boiler Efficiency:
-
Provides major surface area for heat exchange.
-
Operates in subcooled boiling region, meaning water partially turns to steam.
-
Acts as a thermal buffer between high-radiant heat areas (furnace) and lower-temp components (economizer).
Maintenance & Inspection:
-
Soot blowing to clean external tube surfaces
-
Descaling or chemical cleaning of internal deposits
-
Ultrasonic testing for wall thickness
-
Hydro testing for pressure integrity
-
Visual inspection through drum manholes
Boiler Bank vs Other Boiler Tubes:
| Tube Type | Heat Source | Fluid | Main Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiler bank tubes | Convection | Water/steam mix | Steam generation |
| Water wall tubes | Radiation | Water | Furnace heat absorption |
| Economizer tubes | Convection | Feedwater | Preheating |
| Superheater tubes | Convection + Radiation | Steam | Superheating |
Quality & Standards:
-
Manufactured to ASME or EN standards
-
Test certificates for material chemistry, tensile, and hydro tests
-
Proper tube pitch and alignment are critical for performance and flow distribution
Superior Construction and Customizability
Boiler Bank Tubes are crafted using seamless hot-rolled, cold-drawn, or ERW processes for dependable strength and precise dimensions. With options for customizable size, thickness, and length, these tubes suit a wide range of industrial setups, accommodating unique project requirements with tailored finishes and end treatments.
Standards-Compliant and Quality Assured
These tubes are manufactured in strict accordance with ASTM, ASME, DIN, BS, and IS standards. Each batch comes with a test certificate and is subjected to 100% visual, ultrasonic, and eddy current inspections, guaranteeing compliance, traceability, and reliability for critical installations where safety and longevity matter.
Optimal Performance and Application Versatility
Boiler Bank Tubes deliver superior heat exchange and resilience under high working pressures, making them ideal for power generation, heat recovery, and process industries. Their high corrosion resistance, robust structure, and smooth finish ensure efficient operation and minimal maintenance for extended periods.
FAQ's of Boiler Bank tubes:
Q: How are Boiler Bank Tubes customized for various industrial applications?
A: Boiler Bank Tubes are available in a wide range of outer diameters (22 mm to 101.6 mm), wall thicknesses (2 mm to 8 mm), and lengths (up to 12 meters). Custom configurations, finishes, and end treatments, such as plain cut, beveled, or threaded ends, can be tailored to meet specific installation needs.Q: What is the manufacturing process for Boiler Bank Tubes?
A: These tubes are produced using seamless hot-rolled, cold-drawn, or ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) methods, ensuring exceptional strength, dimensional accuracy, and a smooth surface free from defects, with every tube hydro-tested and stress relieved for enhanced performance.Q: When are Boiler Bank Tubes typically used in industrial setups?
A: Boiler Bank Tubes are applied in heat recovery systems, water-tube boilers, steam boilers, and various thermo power generation systems. They are essential components in power plants, process industries, and other sectors requiring efficient heat transfer and reliable operation under pressure.Q: Where should Boiler Bank Tubes be stored to prolong their shelf life?
A: For optimal longevity, these tubes should be stored in a dry, covered area, away from moisture and direct exposure to weather elements. Proper storage ensures they remain free from corrosion and maintain their quality for over five years or more.Q: What benefits do Boiler Bank Tubes offer over standard heat exchange tubes?
A: Boiler Bank Tubes provide superior corrosion resistance (dependent on selected grade), high-pressure operation capabilities, and excellent weldability. Their strict adherence to international standards ensures long-term reliability, safety, and efficiency in demanding thermal environments.Q: Which quality assurance processes are used to inspect Boiler Bank Tubes?
A: Each batch undergoes thorough inspections including 100% visual checks, ultrasonic testing, and eddy current analysis. A test certificate is provided with every batch, ensuring compliance with specified standards and verifying tube integrity before delivery.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Boiler Pressure Part' category
 |
SHREE NARAYAN ENTERPRISE
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese