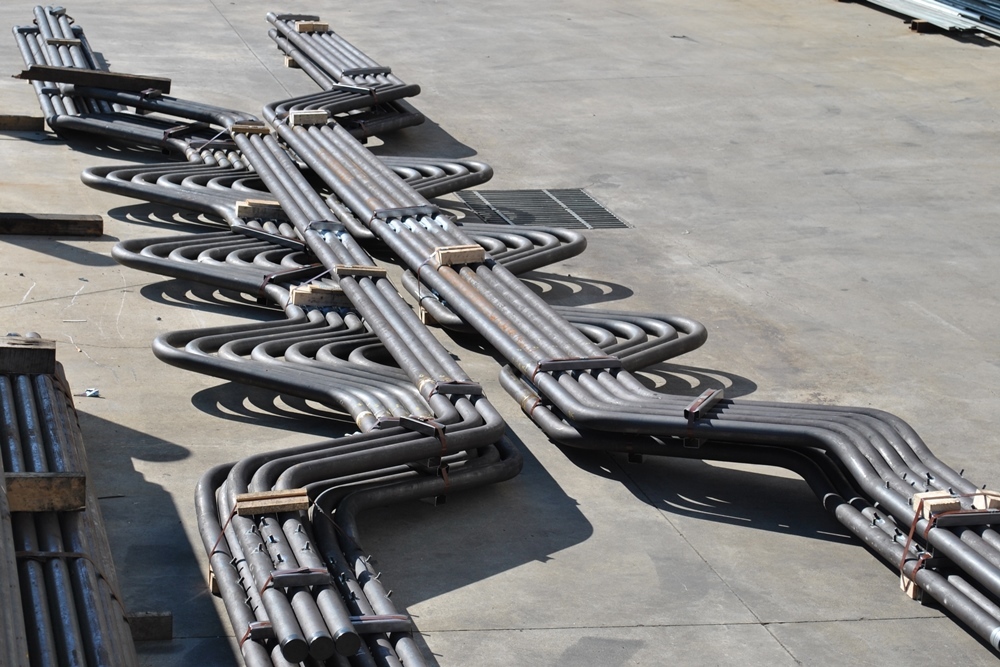
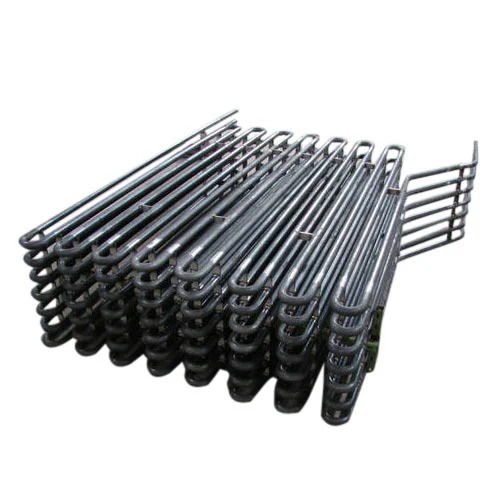
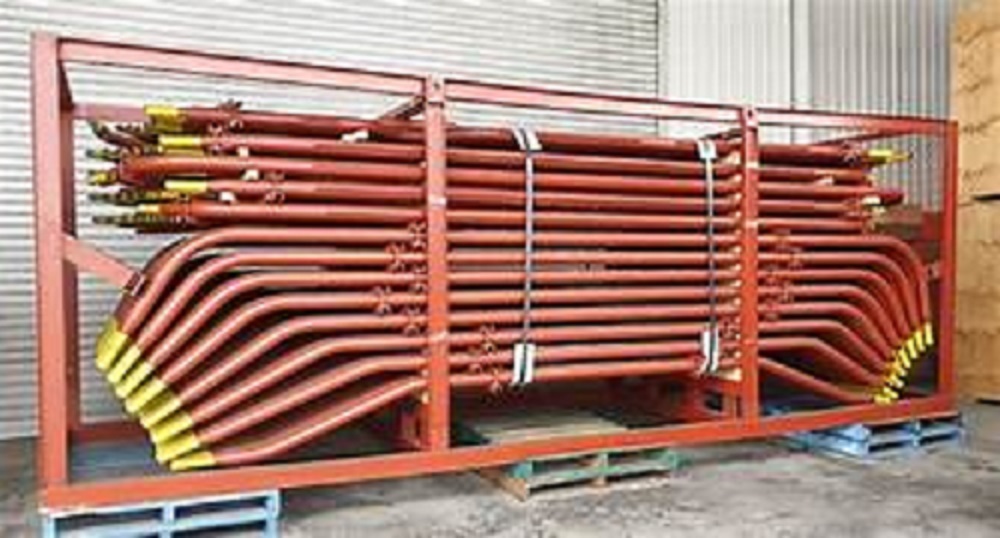
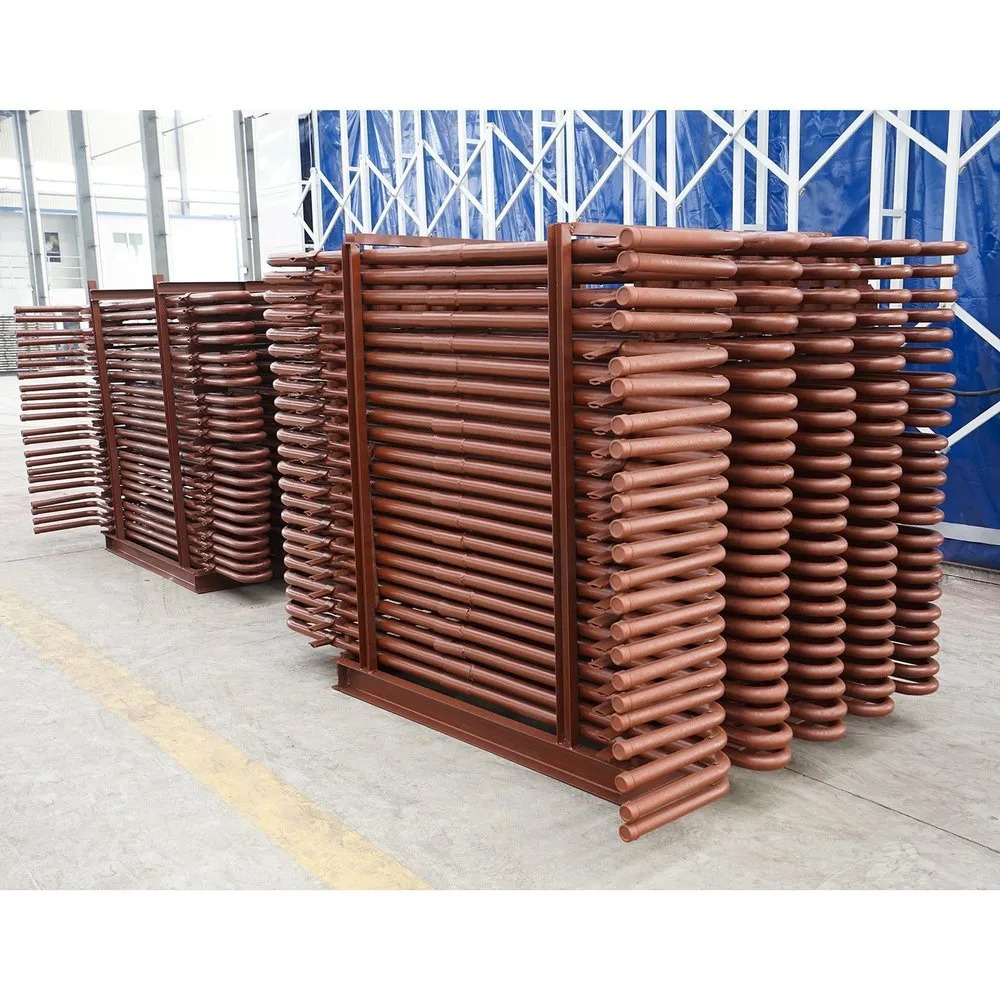
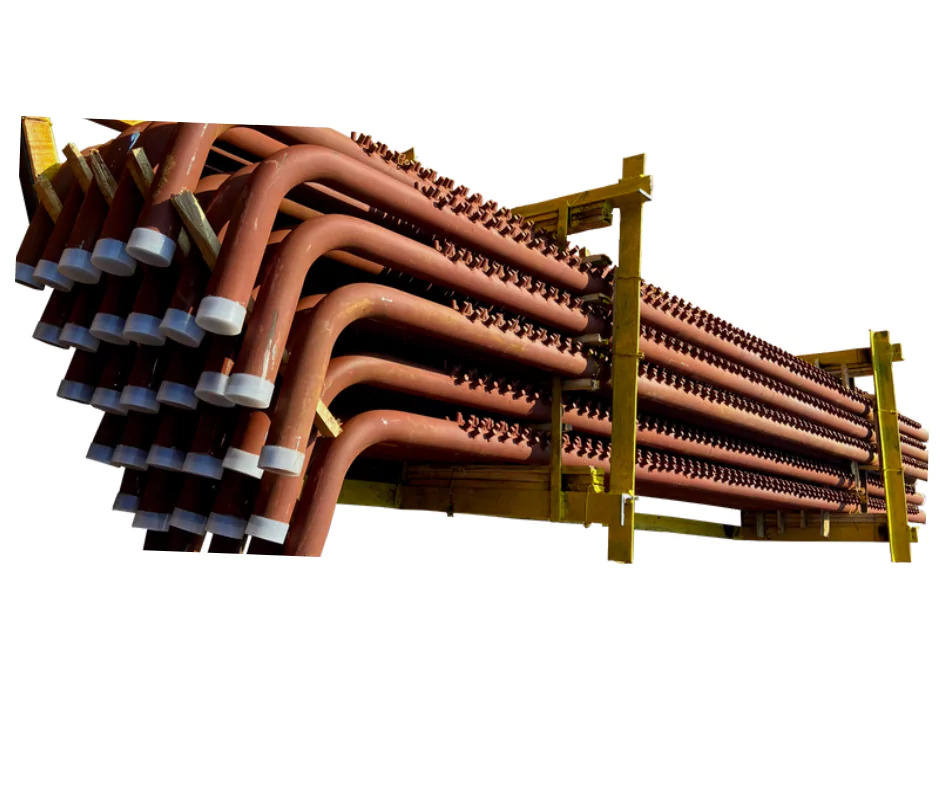
Boiler Tube Bends
Product Details:
- Solubility Insoluble in water
- HS Code 73042900
- Color Metallic grey, black, or as per coating
- Melting Point Varies with material (e.g., carbon steel ~1425C)
- Storage Store in dry, covered conditions to avoid corrosion
- Smell Odorless
- Shelf Life Indefinite under proper storage
- Click to View more
Boiler Tube Bends Price And Quantity
- 10 Unit
- 100000 INR/Unit
Boiler Tube Bends Product Specifications
- Solid, bend/arc tube
- Metallic grey, black, or as per coating
- 73042900
- Industrial, Boiler grade
- Insoluble in water
- NO
- Metallic, smooth finish
- Indefinite under proper storage
- Boiler Tube Bend
- For bending tubes in boilers, heat exchangers, and piping systems
- Varies with material (e.g., carbon steel ~1425C)
- Odorless
- Store in dry, covered conditions to avoid corrosion
Boiler Tube Bends Trade Information
- Vadodara
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- 10 Unit Per Month
- 7 Days
- Yes
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Standard Packing
- Asia
- , All India, South India, Central India, West India, North India, East India, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu, Goa, Jharkhand, Odisha, Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Pondicherry, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
- IBR
Product Description
Boiler Tube Bends Overview
Boiler tube bends are curved sections of tubes used in boilers to route steam, water, or flue gases through various components like economizers, superheaters, water walls, and reheaters. They are critical in connecting straight tube sections while maintaining proper flow and accommodating thermal expansion.
What Are Boiler Tube Bends?
A boiler tube bend is a section of tubing that is bent (usually 45, 90, or custom radii) to form part of a heat exchanger or fluid circuit inside a boiler. They're engineered to:
-
Redirect flow paths
-
Accommodate boiler geometry
-
Handle high pressure and temperature
-
Reduce thermal stress and vibration
Key Applications:
| Area of Boiler | Function of Tube Bends |
|---|---|
| Superheater | Direct steam flow in serpentine coils |
| Economizer | Route feedwater between coil banks |
| Water walls | Link vertical risers to top/bottom headers |
| Reheater | Guide reheat steam through convoluted coil paths |
Specifications & Design:
-
Materials:
-
Carbon steel (e.g., SA-210 Gr A1)
-
Alloy steel (e.g., SA-213 T11, T22)
-
Stainless steel (e.g., TP304, TP316 for corrosive environments)
-
-
Bending Radius:
-
Standard: 3D to 5D (D = outer diameter of the tube)
-
Tighter bends may require mandrel support to avoid wrinkling
-
-
Common Sizes:
-
Outer diameters: 1to 4 or more, depending on the boiler
-
Wall thickness: Designed per ASME Section I or EN standards
-
-
Bend Types:
-
U-Bends
-
Return Bends
-
Elbows (90, 45, custom)
-
Offset bends or serpentine shapes
Manufacturing Process:
-
Cold Bending (for thin walls or low alloy steels)
-
Hot Bending (for thicker, high-strength tubes)
-
Mandrel Bending (for tight-radius, thin-wall bends)
-
Induction Bending (precise control for high-temp applications)
Common Issues with Tube Bends:
-
Wrinkling or flattening at the bend
-
Wall thinning on the outer radius
-
Cracking (especially in alloy steels at high temps)
-
Flow restriction due to poor bend quality
-
Corrosion or erosion in areas of turbulence
Best Practices:
-
Use mandrel-supported bends for tight radii
-
Avoid abrupt direction changes to minimize stress
-
Ensure smooth internal surface for good flow
-
Match bend material to tube material for consistent thermal expansion
-
Account for creep resistance in high-temperature areas (superheaters/reheaters)
Flexible Material Selection for Diverse Applications
Boiler tube bends are available in carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, allowing selection based on specific project requirements. This versatility ensures compatibility with various pressure, temperature, and corrosion conditions, making them ideal for boilers and piping systems in industries ranging from energy to petrochemicals.
Customizable Dimensions and Finishes
Customers can specify bend radius (from 1D to 3D or custom), angles (such as 30, 45, 90, or 180), outer diameters (12mm to 600mm), and wall thickness, providing tailored solutions for varied installation needs. Multiple surface treatment options, including galvanized and oiled finishes, offer enhanced corrosion resistance according to project specifications.
Advanced Manufacturing and Rigorous Testing
Tube bends are produced using hot induction bending, cold forming, or mandrel bending processes, adhering to stringent standards like ASTM, ASME, DIN, and EN. Each bend undergoes thorough inspection-hydrostatic, NDT, visual, and dimensional tests-to ensure consistent quality, safety, and dimensional accuracy for demanding industrial use.
FAQ's of Boiler Tube Bends:
Q: How are boiler tube bends manufactured to meet different project specifications?
A: Boiler tube bends are fabricated using advanced methods like hot induction bending, cold forming, or mandrel bending. The process is chosen based on material and required dimensions, ensuring adherence to international standards such as ASTM A234 or DIN. This flexibility allows customization of bend radius, angle, and wall thickness to match precise project needs.Q: What materials are available for boiler tube bends, and how do I select the right one?
A: Boiler tube bends are offered in carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. The choice depends on your application's temperature, pressure, and corrosion resistance requirements. For example, stainless steel is ideal for high-corrosion environments, while alloy steels suit high-pressure applications. Material selection can be specified during ordering.Q: When should I opt for customized bend angles and radii for my piping system?
A: You may require customized bend angles and radii when your layout does not conform to standard configurations or for optimizing fluid flow and space constraints. Options include 30, 45, 90, 180, and radii from 1D to 3D or tailored values. Customization helps in achieving improved system efficiency and easier installation.Q: Where are boiler tube bends primarily used?
A: Boiler tube bends are principally used in boilers, thermal power plants, petrochemical facilities, oil & gas sectors, and various energy and chemical industries. These bends facilitate efficient directional changes of piping within heat exchangers, steam generators, and large piping networks, contributing to seamless system operation.Q: What testing processes ensure the safety and quality of boiler tube bends?
A: To guarantee durability and reliability, all boiler tube bends undergo thorough testing such as hydrostatic pressure checks, non-destructive testing (NDT), visual inspections, and dimensional verification. These tests are conducted according to internationally recognized standards like ASME and ASTM, confirming each bend's quality and safety for industrial use.Q: How does the surface treatment benefit the performance and longevity of boiler tube bends?
A: Surface treatments-such as oiling, painting, galvanizing, or sandblasting-enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of boiler tube bends. The chosen treatment helps prevent rust in harsh environments, prolongs service life, and meets project-specific performance and appearance requirements.Q: What storage and maintenance practices are recommended for boiler tube bends?
A: Boiler tube bends should be stored in dry, covered conditions to prevent corrosion and damage. With proper storage, their shelf life is essentially indefinite. Regular inspection for surface integrity is advised, especially if the bends are kept for extended periods before installation.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Boiler Pressure Part' category
 |
SHREE NARAYAN ENTERPRISE
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese